More 5. diabetes mellitus images. Some people with prediabetes may have some of the symptoms of diabetes or even problems from diabetes already. you usually find out that you have prediabetes when being tested for diabetes. if you have prediabetes, you should be checked for type 2 diabetes every one to two years. results indicating prediabetes are: an a1c of 5. 7%–6. 4%. Diabetesmellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). glucose is vital to your health because it's an important source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. it's also your brain's main source of fuel. What is type 2 diabetes mellitus? type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease. it is characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood. type 5. mellitus diabetes 2 diabetes is also called type 2 diabetes mellitus and adult-onset diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
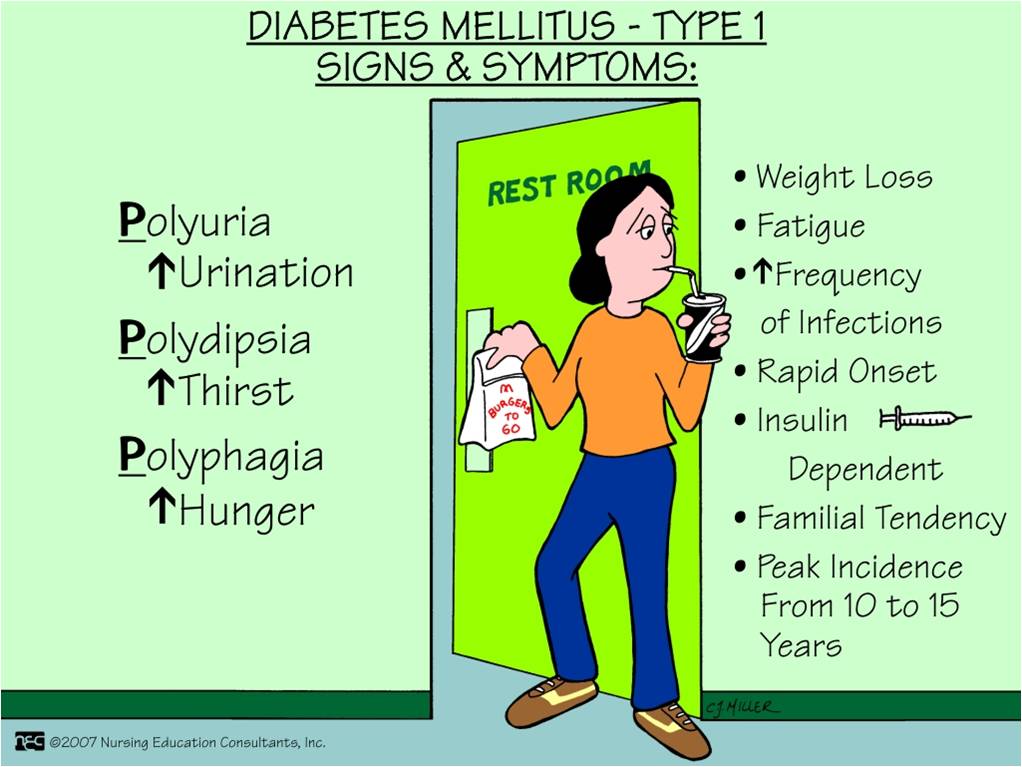
See full list on drugs. com. Diabetes mellitus is a disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat. diabetes occurs in one of the following situations: the pancreas (an organ behind your stomach) produces little insulin or no insulin at all. See full list on drugs. com. Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite.
Diabetes Insipidus Vs Mellitus Differences Symptoms
Diabetesmellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). glucose is vital to your health because it's an important source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. it's also your brain's main source of fuel. the underlying cause of diabetes varies by type. Diabetesmellitus is a condition defined by persistently high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. there are several types of diabetes. the two most common are called type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. during digestion, food is broken down into its basic components. carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, 5. mellitus diabetes primarily glucose. Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong illness. usually, type 2 diabetes is also life-long. however, people with type 2 diabetes can sometimes restore their blood sugar levels to normal just by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and losing weight. gestational diabetes usually goes away after childbirth. however, women with gestational diabetes are at high risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. in people with diabetes, aging and episodic illnesses can cause the body's insulin resist
Diabetes initially might not cause any symptoms. it can sometimes be caught early with a routine blood test before a person develops symptoms. when diabetes does cause symptoms, they may include: 1. excessive urination 2. excessive thirst, leading to drinking a lot of fluid 3. weight loss. people with diabetes also have an increased susceptibility to infections, especially yeast (candida) infections. when the amount of insulin in the blood stream is too low, extremely high blood sugar levels c See more videos for 5. diabetes mellitus. Cluster 5: mild age-related diabetes, most common in elderly individuals. this was the most common form, affecting 39–47 percent of subjects. this was the most common form, affecting 39–47. Diabetesmellitus causes high blood glucose levels and glucose eventually spills into the urine. the glucose spillage causes water loss and thus you have the classic polyuria and polydipsia.
Type 1 diabetes can't be prevented. however, the same healthy lifestyle choices that help treat prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes can also help prevent them: 1. eat healthy foods. choose foods lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber. focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. strive for variety to prevent boredom. 2. get more physical activity. aim for 30 minutes of moderate physical activity a day. take a brisk daily walk. ride your bike. swim laps. if you can't Diabetes is a lifelong illness. however, people with type 2 diabetes can sometimes restore their blood sugar levels to normal just by eating a healthy diet, regularly exercising, and losing weight. aging and episodic illness can cause the body's insulin resistance to increase. as a result, additional treatment 5. mellitus diabetes typically is required over time.
What is diabetes mellitus? diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy. when you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it. On average, insulin is required in half of those with type 1. 5 diabetes within 5. mellitus diabetes four years of diagnosis, compared to over ten years in those with true type 2 (endocrine practice, v7 n5, sept/oct 2001, pgs 339-345).
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat. diabetes occurs in one of the following situations: the pancreas (an organ behind your stomach) produces little insulin or no insulin at all. insulin is a naturally occurring hormone, produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, which. If you have diabetes, see your doctor regularly. people with high blood sugar levels have a higher risk of dehydration. contact your doctor immediately if you develop vomiting or diarrhea and are not able to drink enough fluids. monitor your blood sugar as advised by your health care team. report any significant deviations in blood sugar levels.
Subscribe by Email
Follow Updates Articles from This Blog via Email


No Comments